Difference between revisions of "Z-Force Motor"
From Unofficial Zero Manual
BrianTRice (talk | contribs) |
(No difference)
|
Latest revision as of 22:53, 3 December 2019
-
-
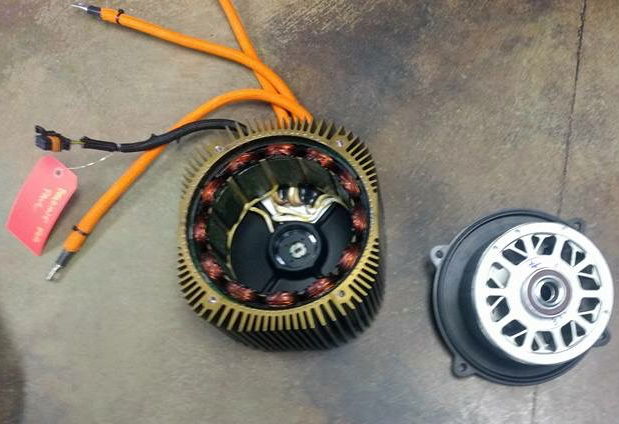

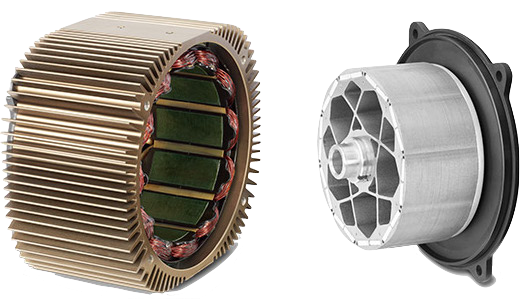
- For the 2013+ models (Gen2 and Gen3), Zero has their own motor design, trademarked "Z-Force".
- Features
- Sealed
- Air-cooled (via finned casing)
- Brushless
- Permanent-magnet rotor
- Operation
- It is a 3-phase brushless DC (BLDC) electric motor which is roughly described as a permanent magnet AC synchronous (PMAC) motor since the controller is continuously adjusting the phase angle of the field to the rotor's current position and speed.
- The field must apply synchronously to the rotor, so the calibration between the position sensor and the controller is critical for efficiency, minimizing wear on the bearings, and minimizing heating of the windings and magnets.
- Motenergy's Clone
- Motenergy makes an unlicensed generic derivative, the ME1507, of the same form factor, rated for much lower outputs and seems to differ from Zero's motor in key ways.
- From Motenergy's ME1507 product page, it's clear that they're advertising a model on par with the 2016 IPM update:
The ME1507 is an Radial Air Gap, Permanent Magnet Synchronous Motor (PMSM) with an Internal Permanent Magnet Rotor (IPM). Designed for battery pack voltages of 100 VDC or less. Maximum rotor speed of 6000 rpm. Continuous current of 200 amps, and continuous power of 17 kw. Weight of 44 pounds.
- Motor theory
- IPM vs SPM for a different motor control regime but some principles translate to the Z-Force motor.
- Efficiency
- forum thread
- Range vs Speed by Patrick Truchon discusses the theory and measurements in depth.
- Does Gear Size Affect Range? by Patrick Truchon with more theory!
- Variants and Revisions